BIOMASS
WHAT IS BIOMASS?
In terms of energy, biomass means those fuels that come from plant debris, either from sustainable forest management of forests or as a byproduct of agriculture.
The main use of biomass is for heat production (and also cold) for heating, hot water production, steam for industrial processes, ...
Unlike fossil fuels, biomass combustion does not add additional CO2 to the natural carbon cycle and, therefore, does not increase the levels of this gas in the atmosphere.
For all purposes it is a 100% renewable energy.
TYPES OF BIOMASS
• The Pellet.These are heavily pressed wooden sawdust pellets in the form of small cylinders. For convenience of use, high availability and dimensioning of the receiving installation in volume and cost, the so-called wood pellet is the most used biomass format at the domestic level.
• The Estella de Fusta.It is obtained from the crushing (chipping) of wood, mainly of forest origin and a subsequent screening and drying process. Estella has low energy density but its simple production and abundance of raw material means that it has a very low energy cost (€ / kWh). Estella is the most widely used biomass format for large installations.
• Firewood.Without, unlike the previous ones, firewood is a fuel that requires more manual intervention, its low cost, both installation and operation, makes it a very competitive solution where automation is not an important aspect.
• Agricultural residuals.Olive bone, almond shell, vine shoots, ... Interesting options in locations close to the corresponding crops and with great availability of these resources.
APPLICATIONS
There are multiple possible configurations of biomass facilities as long as there is a suitable option for a wide variety of projects. For example:
- Heating and hot water production in a family house.
- Centralized heating in apartment blocks.
- Pool air conditioning.
- Distribution network of heat (and cold) in buildings as a whole.
- Heating of farms or greenhouses.
- Steam production for industrial processes.
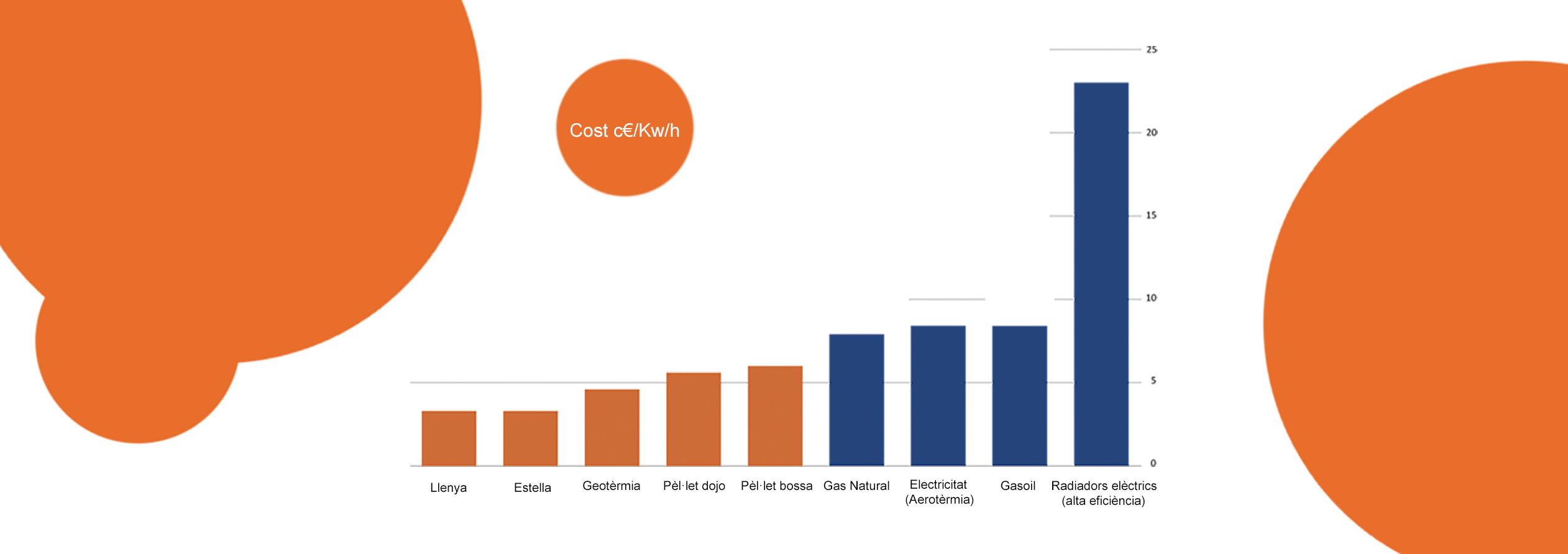
THE 10 REASONS OF THE BIOMASS
- Fuel cheaper than traditional alternatives.
- Price stability. Very favorable evolution forecast due to uncertainty and presumable upward trend in electricity and fossil fuels.
- Reliable and mature technology with a high degree of implementation throughout Europe.
- Flexible solution. It adapts to a wide variety of uses and with a high reaction to variations in thermal demand.
- Efficient solution. High energy yields (> 90%) for different load levels.
- Fully automatic systems, very comfortable for the user.
- Renewable energy source, environmentally friendly.
- Encourages the management of the surrounding forests and, consequently, helps in the fight against forest fires.
- Source of employment and economic activity distributed throughout the territory.
- It allows compliance with the renewable energy quota for thermal consumption required in the Technical Building Code (CTE) and obtains the maximum energy rating: class A.
